Sometimes, for the convenience of the server environment, access to the Internet is prohibited regardless of whether it is a production or test environment. However, this one-size-fits-all approach sometimes brings some inconsistencies to the installation environment, especially when developers need to install dependent libraries on the test environment server. You can’t always spend time manually installing the dependent environment. Therefore, using a proxy server to complete these tasks for the LAN server is much more convenient than mounting ISO images on each machine.
The overall architecture is as follows
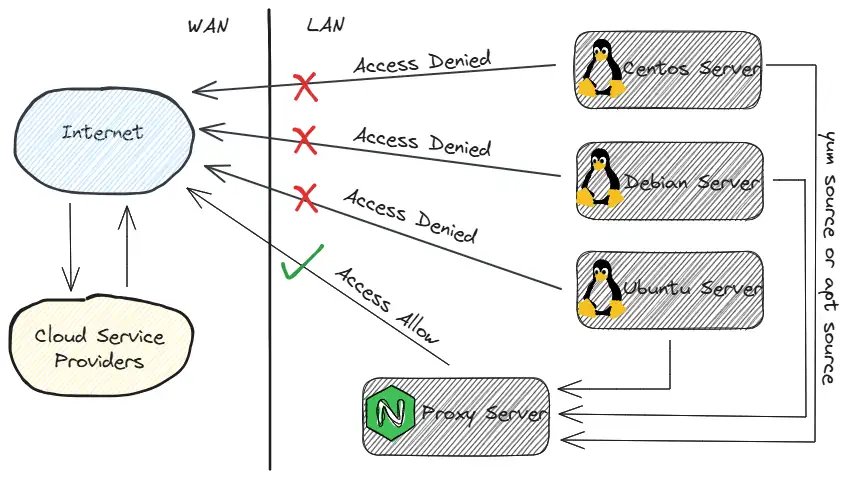 Generally, configure the server network segment to prohibit access to the
Generally, configure the server network segment to prohibit access to the Internet network policy on the hardware firewall, and then add the server{} segment configuration on the Nginx Server.
It is recommended that if you have a LAN DNS server, it is best to add a resolution record. Otherwise, if the yum source or apt source uses the LAN IP address, all configurations may need to be redistributed and updated if the IP address is changed in the future, which is very troublesome.
Edit nginx.conf file
server { listen 443; server_name mirrors.koevn.com; # example
# Other configurations omitted
location /ubuntu/ { proxy_pass http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/; }
location /centos/ { proxy_pass http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/; }
location /debian/ { proxy_pass http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/; }
location /epel/ { proxy_pass http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/; }
# Other configurations omitted
}After the above configuration is completed, verify whether the configuration syntax is correct, and then reload the Nginx service. The LAN yum source or apt source proxy service has been completed.
Next, we will take the Centos 7 operating system as an example. Other distribution operating systems can be configured with slight modifications.
First back up the yum repo file under /etc and then delete it
mkdir -pv /opt/repo_bakmv /etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo /opt/repo_bak/touch CentOS-Base.repo && touch epel.repoEditCentOS-Base.repofile
# CentOS-Base.repo## The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and# geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.## If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the# remarked out baseurl= line instead.##
[base]name=CentOS-$releasever - Base - aliyun.combaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/gpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#released updates[updates]name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates - aliyun.combaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/gpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#additional packages that may be useful[extras]name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras - aliyun.combaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/gpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages[centosplus]name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus - aliyun.combaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/gpgcheck=1enabled=0gpgkey=http://mirrors.koevn.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7Editepel.repofile
[epel]name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearchbaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/epel/7/$basearchfailovermethod=priorityenabled=1gpgcheck=1gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
[epel-debuginfo]name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch - Debugbaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/epel/7/$basearch/debugfailovermethod=priorityenabled=0gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7gpgcheck=1
[epel-source]name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch - Sourcebaseurl=http://mirrors.koevn.com/epel/7/SRPMSfailovermethod=priorityenabled=0gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7Then clear the yum cache and regenerate a new cache
yum clean all && yum makecacheFinally, it is realized that within the local area network, the server without open Internet network permission can also normally install the software dependency environment through yum.
